Fungal infections are common during the rainy season. Humidity and Moisture in the air can be the contributor to the increase in infection during monsoon. Fungal infections occur when an invading fungus takes over an area of the skin, scalp, or nail making their home in these moist areas of the body, especially the folds: between the toes, in the genital area, groin, nails, ear, and under the breasts.
Causative source of Common fungal skin infections is yeasts like Candida or Malassezia furfur dermatophytes, such as Epidermophyton, Microsporum, and Trichophyton These can be a common malefactor of itchy skin.
Causes of fungal infection
Fungal infections are prevalent and the factors responsible are seasonal migration, international travel, and extreme weather. People who are on immunomodulatory agents for treating various diseases like cancer or have excessive sweating, obesity, uncontrolled diabetes, weakened immune system, unhygienic practices are prone to recurrent fungal infections which can be overwhelming and frustrating.
Fungus is all around. Fungi found naturally in the human body or in the environment can grow in humid and moist conditions and can invade and cause infection. However, some fungal infections such as candidiasis and ringworm can spread from person to person through contact. Surface fungal infections are found in the epidermis and mucous membranes, the hair, and the nails. Untreated fungal infections invade deeper layers of the skin and hair follicles and can spread to the blood or internal organs
Symptoms of Fungal skin infections
The presentation of fungal skin infections may vary attributing to the causative fungi and the site of infection. A few of common symptoms are:
- Skin rashes with raised or bumpy edges.
- Redness, blisters
- Soreness, Itching, stinging or burning sensations
- Peeling skin
- Cracking skin
- Pain in the inflamed body part (ear, foot, nail, scalp, etc.)
- Breaking and loss of infected hair
- Disintegrated and brittle finger and toe nail sometimes with discoloration.
Diagnosis
The dermatologist usually diagnoses a fungal skin infection by examining the infected area which usually is inflamed itchy or scaly. A confirmatory test is conducted by taking a small portion of skin tissue, a scrap of nail or an offcut of hair and examining it under a microscope or placed in a culture medium where the specific fungus can grow and be identified. Blood tests are also recommended in case of severe infection.
Treatment of fungal infections
Treatment of fungal infections
Most fungal skin infections can be treated with ease if diagnosed early and treated in time. The first line of treatment is antifungal drugs; usually these antifungal drugs are applied directly to the affected area. These over the counter and prescribed topical drugs include creams, gels, lotions, solutions, or shampoos. Depending on the severity of the infection oral Antifungal drugs can be added as a combination therapy. In severe infections, certain drugs like corticosteroids are used for a short period of time to relieve inflammation and itching. The duration of treatment may vary depending on the severity and site of infection from two to eight weeks to up to a year and a half.
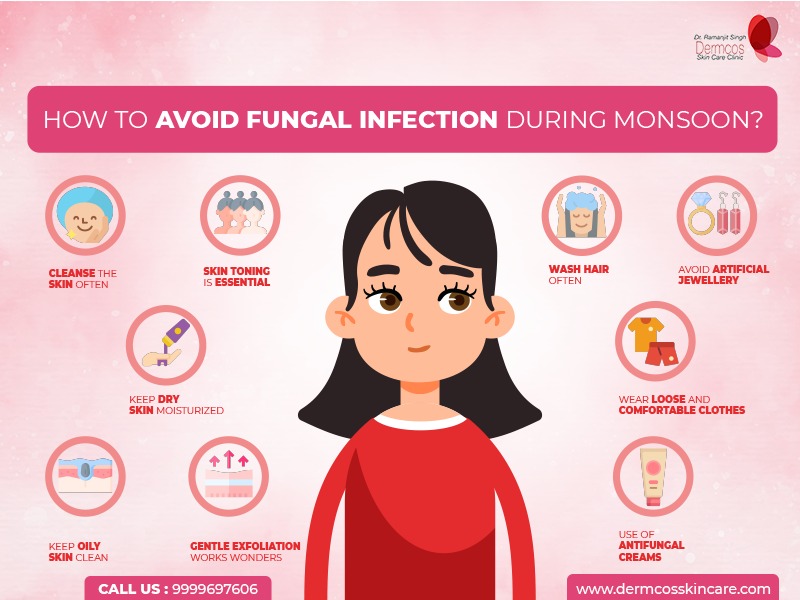
Prevention is better than cure!
Preventive action can be taken to avoid fungal skin infections and its recurrence!
• Maintain basic hygiene.
• Keep the skin clean and dry.
• Wash undergarments, socks, clothes, towels and bed linen regularly with detergent and mild antiseptic and sundry. Preferably iron the undergarments before wearing
• Wear comfortable clothing like cotton, mulmul and avoid contact with perspective carriers
• Do not share toiletries and personal grooming items like towels hair brushes combs and sporting equipment.
• Remove shoes every three to four hours giving them time to dry out.
• Use extra absorbent socks.
• Do not walk barefoot.
• Use of coconut oil or moisturizer.
If you have the tendency of skin rashes especially during the monsoon visit a qualified Dermatologist and get timely treatment and enjoy hassle free monsoon.


